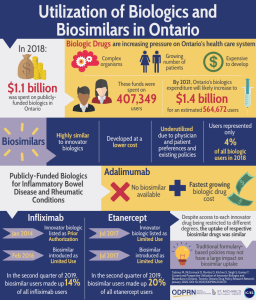
Biologic drugs are important treatment options across a wide number of medical conditions, including rheumatic conditions, gastrointestinal disease, and diabetes. Although these drugs have had a measurable impact on patient outcomes, their substantial cost and growth in use threatens the sustainability of public drug programs. A biosimilar biologic drug, or biosimilar, is a drug that is highly similar and has no clinically meaningful differences to an innovator biologic. Biosimilars can also be developed at a lower cost and therefore offer an opportunity to reduce public drug spending.
Unfortunately, biosimilars are underutilized and as a result, public payers in Canada have begun developing policies designed to increase the use of biosimilar drugs. Essential to this work is a better understanding of the use of biologics and biosimilars across various medical conditions.
This report describes the current and prospective utilization patterns and expenditures of innovator biologics and biosimilars through the public drug program in Ontario, Canada.
CADTH summarizes this report in “Utilization of Innovator Biologics and Biosimilars for Chronic Inflammatory Diseases in Canada: A Provincial Perspective” and discusses potential implications for decision-makers.
Access the full article and associated resources: